 Seitenverzeichnis
Seitenverzeichnis
 Site
map
Email
Site
map
Email
Content




The Rainforest
Afrika
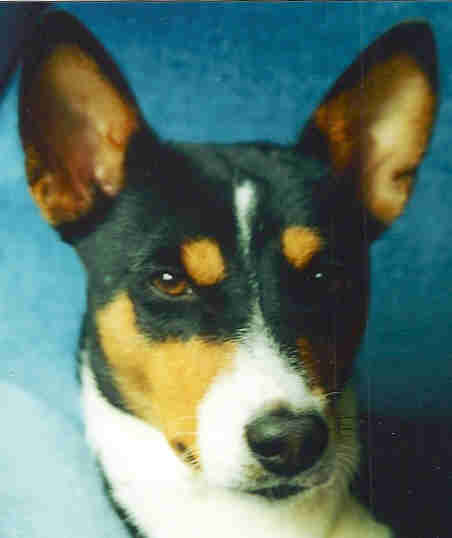
Dog Tjesem Congo
Terrier
Prototype
Dog

Dzanga Sangha Nationalpark cocan.de The homeland of the pygmies and the Basenjis is threatened. The rainforest is being drastically reduced with consequences for various species and the global climate.
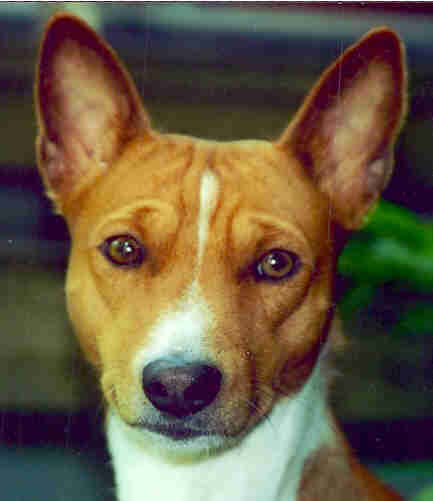
"Basenjis the barkless dogs "
Veronica Tudor Williams

Schensi dogs are hunting helpers at the Efe and the BaAka. The pygmies trained basenjis as hunting dogs for their settled neighbors the Bantus and got food especially bananas therefore.Basenjis
1987 Net Hunting group with Basenji in the Rainforest
Courtesy Picture Michael Work
Pygmies Net Hunting in the Ituri Rainforest
with Success
Photos Armin Heymer Die Pygmäen Vlg. List
The hunt should be more successful if several groups combine to build a larger netting wall, i.e. 100m (300 ft.)After a successful hunt, the Basenjis storm ahead with clanging bells into the camp and so announce the success of the enterprise. If the hunt was without results, the bells are silenced by stuffing them with grass.
Basenji with a
bell
Photo William F Wheeler 1990
The Basenjis were used as hunting dogs in their natural homeland, independent to do their duty. Without their assistance the spear hunting for Elephants and other large wild animals would be impossible. In the rain forest with all its dangers they have to be able to independently take care of their food and survival. When the hunt was successful they were thrown a few unwanted bits.
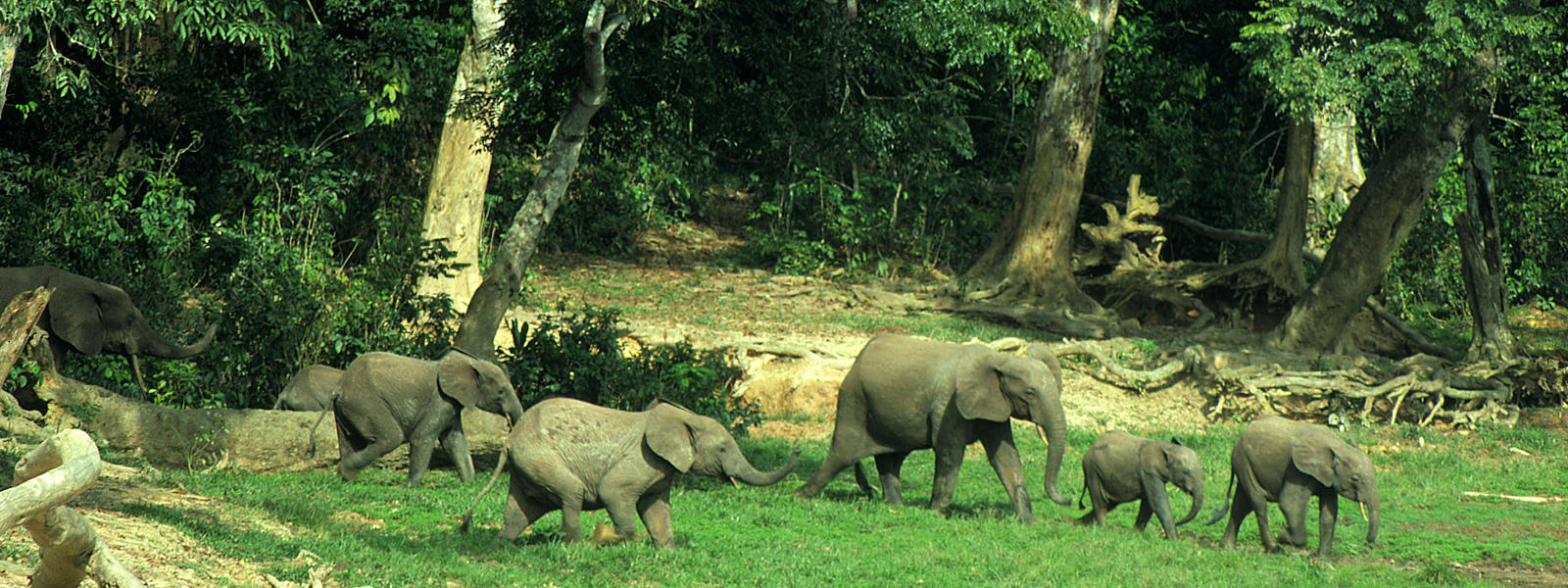
The mysterious forest elephant in the rainforest of Africa



http://worldwildlife.org/species/forest-elephant
The Forest-Elephant "Dwarf Elephant"
"The WWF is campaigning for the co-existence of forest elephants and the local population, as well as for the protection of the natural habitat of these small giants. Only in large unbroken areas of rain forest is the existence of pygmy elephants guaranteed. Along with the prairie elephants, the legendary forest elephants live in Africa. Other descriptions of the forest elephant are “round eared elephant”, “dwarf elephant” and “pigmy elephant”.
Because of their hidden lives, one still does not know much about these secretive animals. They are seldom seen because in the dense forest visibility is so limited that they usually flee from any confrontation. In contrast to the three to four meter shoulder height of the grassland elephant, the forest elephant has only a shoulder height of two to two and one half meters. A few of them are even less that two meters high. Their ears are relatively small and round. Their tusks are long, thin and only slightly curved. In the thick jungle, a smaller body and downwards pointing tusks are an advantage. And make the forest elephant much more agile.
The rain forest provides the elephants with all the food and water they need. They eat fruits, branches and herbs of over one hundred fifty varieties. Forest elephants often migrate to the areas where their beloved fruit trees grow. At the same time they spread the population of these trees through the undigested seeds in their dung. A few of these tree species are only capable of growth after their fruits have been eaten. Without the forest elephants these trees would disappear. One is rarely lucky enough to observe forest elephants outside of the forest."
Natural environment is the Ituri Rainforest. The Rainforest is threatened.
You can help with this program
panda.org/what_we_do/endangered_species/elephants/african_elephants/

The owner of this site assumes no liability for the content of its website links.
The linked sites are the sole responsibility of their owners.